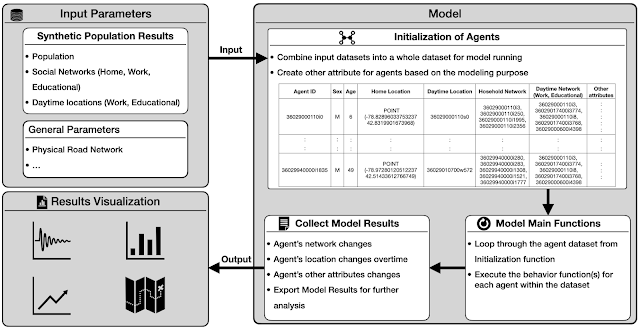
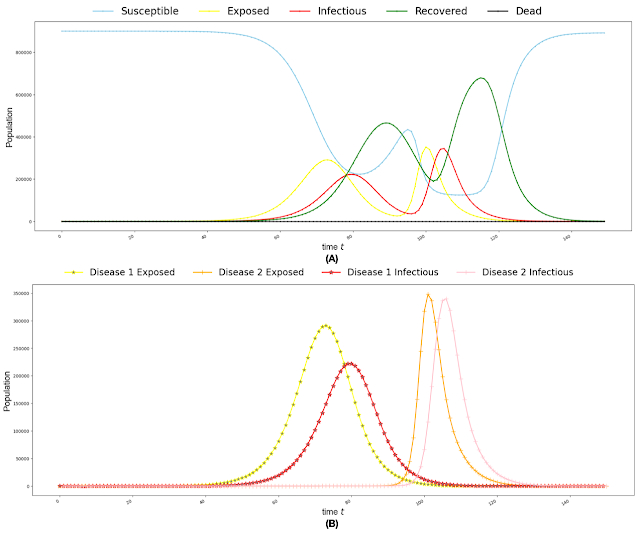
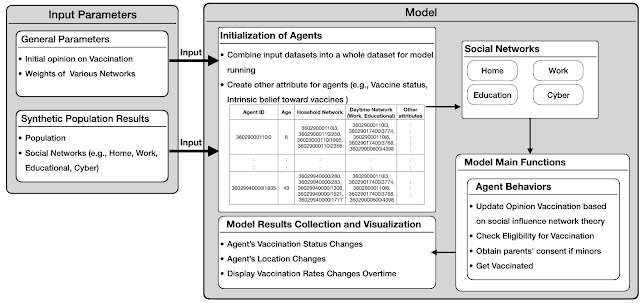
Sessions Abstract:
There is an urgent need for research that promotes sustainability in an era of societal challenges ranging from climate change, population growth, aging and wellbeing to that of pandemics. These need to be directly fed into policy. We, as a Geosimulation community, have the skills and knowledge to use the latest theory, models and evidence to make a positive and disruptive impact. These include agent-based modeling, microsimulation and increasingly, machine learning methods. However, there are several key questions that we need to address which we seek to cover in this session. For example, What do we need to be able to contribute to policy in a more direct and timely manner? What new or existing research approaches are needed? How can we make sure they are robust enough to be used in decision making? How can geosimulation be used to link across citizens, policy and practice and respond to these societal challenges? What are the cross-scale local trade-offs that will have to be negotiated as we re-configure and transform our urban and rural environments? How can spatial data (and analysis) be used to support the co-production of truly sustainable solutions, achieve social buy-in and social acceptance? And thereby co-produce solutions with citizens and policy makers.
Session 1 (Date: 4/16/2024; Time: 10:40 AM - 12:00 PM; Room: 312 (Ni`ihua), Third Floor, Hawai'i Convention Center)
Chair: Na (Richard) JiangPresentions:
- Bright Addae and Suzana Dragicevic,
- Hui-Chun Lee and Tzai-Hung Wen:
- Sean C Ahearn,
- Alison Heppenstall, Gary Polhill, Mike Batty, Ricardo Colsanti, Matt Hare, Richard Milton and Doug Salt,
- Jacqueline Kazil, Boyu Wang and Thomas Pike,
Session 2 (Date: 4/16/2024; Time: 1:20 PM - 2:40 PM; Room: 312 (Ni`ihua), Third Floor, Hawai'i Convention Center)
Chair: Suzana Dragicevic- Yenny Andrea Cuellar Roncancio and Liliana Perez,
- Farzin Lotfi-Jam and Jenni Minner
- Duo Zhang, Raja Sengupta and Antonia Gieschen
- Na (Richard) Jiang and Andrew Crooks
- Yuan Feng, Ying Miao, Ed Turner and Yu Jia